What is Disperse Dye?
Disperse dyes are non-ionic colorants with low water solubility that, in their disperse colloidal form, are suitable for dyeing and printing hydrophobic fibers and fabrics like cellulose acetate (CA), Polyester (PE), Nylon etc.Because these dyes are present in the dye bath as a fine aqueous suspension in the presence of a dispersing agent so these are known as Disperse Dye.
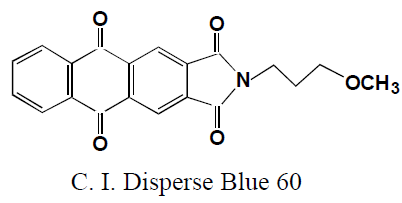
Some example of Disperse Dye-
Properties of Disperse Dye:
- Disperse Dyes are non-ionic organic compound of relatively low molecular weight.
- These are insoluble in water at low or room temperature and have only limited solubility at higher temperatures.
- They have substantivity for hydrophobic fibres such as nylon and polyester, in which they are quite soluble.
- These dyes are present in the dye bath as a fine aqueous suspension in the presence of a dispersing agent.
- Many of these dyes 130°c sublime on heating and dyeing.
- Disperse dyes have slight water solubility because of the presence of polar substituents in their molecular structure.Typical example of these
- Typical example of these substituents is hydroxy-ethyle-amino groups (–NHCH2SO3Na).




nice blog for Disperse Dye and Properties of Disperse Dye, i am impress this concept, disperse blue , i have work on this
ReplyDeletethis really help me alot.
ReplyDeletefabrics manufacturers
Post a Comment